EXAM: BANGLADESH BANK POST: ASSISTANT DIRECTOR DATE: 31.07.2015 TOTAL MARKS: 200 TIME: 120 MINUTES
Question 01: Write an essay on ‘Debt Crisis in Greece.
Solution: The Greek government-debt crisis (also known as the Greek depression) started in late 2009. was the first of five sovereign debt crises in the eurozone – later referred to collectively as the European debt crisis. In Greece, triggers included the turmoil of the Great Recession, Structural weaknesses in the Greek economy , and sudden crisis in confidence among lenders.
In late 2009, fears developed about Greece’s ability to meet its debt obligations, due to revelations that previous data on government debt levels and deficits had been misreported by the Greek government. This led to a crisis of confidence, indicated by a widening of bond yield spreads and the cost of risk insurance on credit default swaps compared to the other Eurozone countries – Germany in particular. In 2012, Greece’s government had the largest sovereign debt default in history. In the recently held government election in Greece, public showed their opinion for being with The Euro zone. Debt burdened Greece has many problems. The newly elected government tried to recoup it for taking huge amount of financial assistance from the master countries of Euro zone such as German, France which will expedite the economic reforms of the debt burdened country. Austerity taken by the then prime minister exasperated the people as general people don’t like to sacrifice for their country. International lending institutions like World Bank and International monetary fund have already warned Greece to repay their debt amount without considering the country’s prevailing conditions or situation. As a result, the country entangled with a great financial crisis. But people gave their nods or consent in the recently held yes/no election-whether they will remain with Euro zone or not. Finally they reached a decision. A long awaited treaty with Euro zone has already been made providing Greece with a huge a amount of financial facilities which strengthened the bond between Greece an Euro zone.On June 30, 2015, Greece became the first developed country to fail to make an IMF loan repayment. At that time, Greece’s government had debts of €323bn.
Question 02. Brain drain also termed as human capital flight, is a phenomenon where skilled and qualified people of developing countries to serve there. Many people are against it and argue that it decreases the skilled workforce of a country for a rich one and slows down its development.’ What is your opinion about it?
Solution: Human Capital Flight or Brain Drain
Human capital flight, sometimes called brain drain, refers to the emigration of intelligent, welleducated individuals for better pay or conditions, causing their places of origin to lose skilled people, or ‘brains’. Typically, such emigrating individuals have learned English and have moved to the United Kingdom, the United States or some other English-speaking country. An example is Albert Einstein. Brain drain is common in developing nations. China and India have recently topped the list of those nations experiencing an exodus of skills and intelligence through human capital flight.
Types of Brain Drain
Organizational: The flight of talented, creative, and highly qualified employees from large corporations-e.g. Yahoo, Google, HubSpot, and Microsoft- that occurs when employees perceive the direction and leadership of the company to be unstable or stagnant, and thus, unable to keep up with their personal and professional ambitions.
Geographical: The flight of highly trained individuals and college graduates from their area of residence, for instance, those migrating from the mid-western United States to the coastal states and large metropolises.
Industrial: The movement of traditionally skilled workers from one sector of an industry to another. For example, jobs in the United States and other governments, also known as the public sector, have her governm experienced significant generational brain drain as tenured boomer generation employees retire. Heightened competition for talent from the private sector and budgetary constraints have made it increasingly difficult to attract replacements for these retirees.
Causes of brain drain
As with other human migration, the social environment is considered to be a key reason for this population shift. In source countries, lack of opportunities, political instability or oppression, economic depression, health risks and more contribute to brain drain, whereas host countries usually offer rich opportunities, political stability and freedom, a developed economy and better living conditions that attract talent. At the individual level, family influences (relatives living overseas, for example),as well as personal preferences and caeer ambitions and other motivating factors can be considered.
Advantages of the brain drain
A brain drain is effectively an export of human resources such as “education services”, which has inadvertently “become a money machine for countries such as the US, contributing over $7 billion to the US economy”. However, it is important to note that the knowledge and wealth generated is twofold, both for the country of origin and the host country, which acquires additional human capital to fill labour gaps, thus increasing economic development. The country of origin, exporting their skilled and highly educated workforce, benefit from a brain gain both in terms of the increase in the labour power they possess, and also in the fact that “skilled migrants leaving the country generate
increased demand for higher level education amongst the population”. Furthermore, the sending back of remittances increases economic development in the country and its standard of living. Circular migration presents a number of benefits associated with brain drain. First, the economy of the origin country may not be able to take advantage of the skilled labourers, so it becomes more beneficial for the workers to migrate and send back remittances. Second, when the migrant workers return home as part of the circular pattern, they may bring with them new skills and knowledge. Remittances are a positive effect of the brain drain because they increase living standards in society. The remittance economy is a significant part of the brain drain as well an integral source of income for developed economies.
Negative consequences of brain drain
While a brain drain is beneficial, its flaws are inherent in its title, since it usually involves the loss of human capital, i.e. a skilled labour force which is vital to the development of society and the country as a whole. Emigration of these skilled workers as “essentially providing personal benefits for individuals rather than public benefits”.
The brain drain benefits individuals more than society. However, implementing policies to reduce their movement is in effect to act against the process of development. This means society is inadvertently caught in many negative scenario, whereby allowing the Brain Drain to continue is likely to result in knowledge being distributed unevenly’ across space, resulting in a fall in economic development for either the country of origin or destination countries.
Another consequence of the brain drain is the existence of social marginalisation, which occurs due to several reasons. For example, highly skilled labourers have been villainised by society because they may be perceived as a disruption to existing society. The migrants themselves, who have struggled to adapt to their new surroundings and way of life, may subsequently perceive themselves as living ‘parallel lives’.
Question 03.Read the following passage and answer the questing
Polythene bag is certainly the most popular carrying container in our country Jute gunny bags and the likes of it are on the verge of extinction before the practical utility of the polythene bags. The reasons are quite simple. They are cheap, easy to handle and convenient. In a lower middle-income country like ours, it is only natural that low price of polythene bag is more than enough reason for its being the favorite one. Moreover, polythene bag is available everywhere. Then why should one go for something else? In spite of all its utility, it cannot be denied that polythene is causing havoc on our environment. We are accustomed to throwing polythene bag anywhere and everywhere as soon as their need is over. On an average 55 lakh pieces of polythene bags are being used in Dhaka city alone. Most of this huge quantity of used and then thrown-out polythene bags find their way into the drains and sewerage pipe blocking the easy and regular flow of waste which might result in the complete breakdown of the drainage system. In fact we often see the horrible sight of waste and poisonous wat gushir out of the manholes and flooding nearby places. Again, during the rainy season, this kind of blockage by polythene bag poses interruption on the way of rain water flowing to the drains. And it mainly because of the polythene that many low lying areas of Dhaka city are submerged in water. In this regard, we can recall arguably the long lasting flood in 1998
when flood water remained in many parts of Dhaka for over two months. Polythene bag is also a potential threat to our cultivable land as it is not biodegradable (capable of being decomposed by natural means). And it is because of this characteristic that polythene does not mix with soil, it remains unchanged like a strong curtain through which nothing can pass. As a result, natural working of the different elements in soil is obstructed that ultimately weakens the fertility of soil. However, it is a happy news that the ban on production, distribution and marketing of polythene shopping bags has already been imposed throughout the country. The common citizens also responded in welcoming the move.
a) What is the main idea of the passage?
Solution: The main idea of the passage is the merits and demerits of polythene bags on environment. Using polythene bags indiscriminately and throwing it here and there has a immense environmental effect which cannot be denied. As polythene bag is a one kind of chemical (inorganic materials) which is not decomposed with the soil, it reduces the fertility of soil. On the other hand, for its easy and convenient uses, polythene’s are being used everywhere.
b) What is on the verge of extinction? Why is it on the verge of extinction?
Solution: Jute gunny boys and products which are made by jute are on the verge of extinction because the alternative products are available which are cheap, easy to handle and convenient.
c) What are the reasons of polythene bags being popular among the citizens?
Solution: Among others carrying container in the country polythene is the famous one. As the country is growing fast industrially, lands are being occupied by the industries in which polythene are made. Besides comparing to the prices of jute made products, polythene are cheap and light in weight. So, people can easily carry it. Thus polythene got popularity.
d) How does the use of polythene bags affect the fertility of cultivable land?
Solution: As polythene bags are inorganic chemical materials it hardly gets mixed with soil. It remains unchanged like as strong curtain through which nothing can pass and we know nitrogen is a very essential element of soil and air. If these two elements do not get nitrogen, soil does not get nutrition. As a result, fertility of cultivable lands decreases.
e) How does the use of polythene bags affect the drainage system?
Solution: On an average 55 lakh pieces of polythene bags are being used in the Dhaka city alone. This quantity of polythene bags are dumped into the drains and sewerage pipe which causes blockading of drainage system. It affects the drainage system greatly.
f)How should the citizens modify their behavior to solve the problem?
Solution: At first, we have to think for the long run. It we think about the present utilization of polythene bags, we will not be able to realize the consequences of using polythene bags as it has a harmful effect on environment. As it lessens the quality of soil, so we should avoid using polythene as a mean of carrying container.
Question 04.Solve the following problems.
a) A bus was hired at the cost of Tk. 2,400 and it was decided that every student would share the cost equally. But 10 more students joined and as a result the fare decreased by Tk. 8 per person. How many students were travelling in the bus?
Solution: অনুবাদঃ 2,400 টাকা দিয়ে একটি বাস ভাড়া করা হলো এবং সিদ্ধান্ত নেয়া হলো যে, প্রত্যেকেই সমান খরচ বহন করবে। কিন্তু আরো 10 জন ছাত্র যোগ দেয়ায় মাথাপিছু খরচ ৪ টাকা করে কমে গেল। ঐ বাসে কত জন ছাত্র ভ্রমণ করেছিল?
Let, the number of students be=x
Then the per student cost was =$\frac{2400}{x}$=TK
After joingto students total number of student (x+10)then the per student cost decreased to
$\frac{2400}{x+10}$
According to question,
$(\frac{2400}{x}-\frac{2400}{x+10})$=8
$\frac{300}{x}-\frac{300}{x+10}$=1
$\frac{300(x+10)-300x}{x(x+10)}$=1
300x+3000-300x=$x^{2}$+10x
$x^{2}+10x-3000$=0
x(x+60)-50(x+60)=0
(x+60)(x-50)=50
x=50
x=-60(which is not acceptable)
the number of student who were travelling is (x+10)=50+10=60 ( ans)
b) The average age of students of a class is 15.8 years. The average age of boys in the class is years and that of the girls is 15.4 years. Find the ratio of number of boys to the number of in the class.
Solution; অনুবাদঃ একটি Class এ ছাত্রছাত্রীদের বয়সের গড় 15.8 বছর। Class এ ছাত্রদের বয়সের গড় 16.4 বছর এবং ছাত্রীদের বয়সের গড় 15.4 বছর। ঐ Class এ ছাত্রছাত্রীর সংখ্যার অনুপাত কত? Let, the number of boys is =x and the number of girls is = y
According to question
16.4x + 15.4y = 15.8(x + y)
→ 16.4x + 15.4y = 15.8x+15.8y
→ 16.4x-15.8x = 15.8y – 15.4y
→ 0.6x = 0.4y
→ 6x = 4y
$\frac{x}{y}=\frac{4}{6}$
The ratio of number of boys to the number of girls in the clas is 2 : 3.( ans.)
c) If $x+\frac{1}{3}$ = 3, then the value of $(x^{6}+\frac{1}{X^{6}})$=?
solution:( $x+\frac{1}{3}$)=3
Now,$\left( x^{6}+\frac{1}{x^{6}} \right)$
=> $(x^{2})^{3}+(\frac{1}{x^{2}})^{3}$
$\Rightarrow \left( x^{2} +\frac{1}{x^{2}}\right)^{3}-3.x^{2}.\frac{1}{x^{2}}\left( x^{2} +\frac{1}{x^{2}}\right)$
$\Rightarrow \left( x^{2}+\frac{1}{x^{2}} \right)^{3}-3\left( x^{2}+\frac{1}{x^{2}} \right)$
=> $\left( \left( x + \frac{1}{x} \right) – 2x \cdot \frac{1}{x} \right)^3 – 3\left( \left( x + \frac{1}{x} \right) – 2x \cdot \frac{1}{x} \right)$
=> $\left( 3^{2}-2 \right)$ – 3 $\left( 3^{2}-2 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \left( 9-2 \right)^{3}-3\left( 9-2 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \left( 7 \right)^{3}-3.7$=343-21=322(ans)
d) The percentage profit earned by selling an article for Tk. 1,920 is equal to the percentage loss incurred by selling the same article for Tk. 1,280. At what price should the article be sold to make 25% profit?
অনুবাদঃ কোন একটি পণ্য 1,920 টাকায় বিক্রয় করায় শতকরা যে পরিমাণ লাভ হয় 1,280 টাকায় বিক্রয় করলে ঠিক ঐ পরিমাণ ক্ষতি হয়। 25% লাভ করতে হলে দ্রব্যটি কত টাকায় বিক্রয় করতে হবে?
Solution:
Let, the cost price be Tk. x
So, Profit=Selling price-Cost price.
& Loss = Cost price-Selling price. Now, According to question
1,920-x=x-1,280
=> x+x=1280+1920
=>2x=3200
so, x=1600
The cost price of the article is Tk. 1,600.
Now at 25% profit, the selling price will be = ( 1600 + 1600x $\frac{25}{100}$Tk.
= (1,600 + 400) Tk. = 2,000 Tk. (ans.)
e) A can do a piece of work in 10 days, while B alone can do it in 15 days. They work together for 5 days and the rest of the work is done by C in 2 days. If they get Tk. 4,500 for the whole work, how should they divide the money?
অনুবাদঃ A একটি কাজ 10 দিনে করতে পারে, যেখানে B কাজটি 15 দিনে করে। তারা একত্রে 5 দিন কাজটি করে এবং কাজটির বাকি অংশ C করে 2 দিনে। যদি কাজটির জন্য 4,500 টাকা পাওয়া যায়, তবে কে কত পাবে?
Solution:
(A + B)’s 5 days work
=> 5$\left( \frac{1}{10}+\frac{1}{15} \right)$
Remaining work = 1-$\frac{5}{6}$
C’s 2 day work=$\frac{1}{6}$
Now, A’s 5 days work: B’s 5 days work: C’s 2 days work
= $\frac{1}{10}\times 5:\frac{1}{15}\times5:\frac{1}{6}$
=$\frac{1}{2}:\frac{1}{3}:\frac{1}{6}$ [6 দ্বারা গুণ করে]
=3:2:1
so, A’s share = $\frac{3}{6}\times 450$ = 2,250 Tk.
B’s share= $\frac{2}{6}\times4500$ = 1,500 Tk. –
C’s share=$\frac{1}{6}\times 450$=750 TK
(ans): A’s share 2,250 Tk.; B’s share 1,500 Tk.; C’s share 750 Tk.
f) ABCD is a square and one of its sides AB is also a chord of the circle as shown in the figure. What is the area of the square?
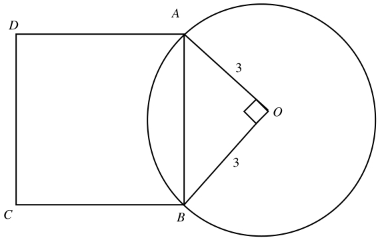
অনুবাদঃ ABCD একটি বর্গক্ষেত্র এবং AB হলো বৃত্তের জ্যা। বর্গক্ষেত্রের ক্ষেত্রফল কত?
Solution:
চিত্রে যেহেতু, $\angle$AOB = এক সমকোণ
তাই ABO একটি সমকোণী ত্রিভুজ যার AB অতিভুজ ।
পিথাগোরাসের সূত্রানুযায়ী,$AB^{2}=AO^{2}+BO^{2}$
$\Rightarrow AB^{2}=3^{2}+3^{2}$
AB=18
$\Rightarrow AB^{2}=\sqrt{2\times 9}$
$AB=3\sqrt{2}$
অর্থাৎ বর্গক্ষেত্রের একবাহু পাওয়া গেল 3 √2.
অতএব বর্গক্ষেত্রের ক্ষেত্রফল = (বাহু)² বৰ্গএকক = $\left( 3\sqrt{2} \right)^{2}$ বর্গএকক = 9 × 2 বর্গ একক= 18 বর্গএকক।(ans)
Question 05.আয় বৈষম্য দূরীকরণে ব্যাংকের ভূমিকা’ – বিষয়ে বাংলায় একটি রচনা লিখুন।
Solution: স্বাধীনতা পরবর্তী সময়ের পর থেকে এ পর্যন্ত পালা বদল করে বিভিন্ন সরকার বিভিন্ন সময় এ দেশ শাসন করেছে। তারা তাদের শাসন কার্যপরিচালনায় বিভিন্ন উন্নয়ন নীতিমালা গ্রহণ করেছেন, যেমনঃ দারিদ্র্য বিমোচন কৌশলগত (PRSP), পঞ্চবার্ষিকী পরিকল্পনা ইত্যাদি। এসকল পরিকল্পনার মেয়াদ শুরু হয়ে শেষ হয়েছে, কিন্তু এদেশের মানুষের ভাগ্যাকাশে এখনও শুকতারা জ্বলে উঠেনি। ধনী ক্রমশ তাদের ধন-বিত্ত-বৈভব বাড়িয়ে পাহাড়সম আকার ধারণ করছে। আর গরীব ধীরে ধীরে শীর্ণকায় হয়ে অস্তিত্বের জন্য সংগ্রাম করছে। প্রতি বছর জিডিপির আকার বাড়িয়ে দেখানো হলেও মানুষের জীবনযাত্রার মানের কোনোরূপ পরিবর্তন হয়নি। আয় বৈষম্য দিনে দিনে প্রকট থেকে প্রকটতর রূপ ধারণ করছে। এই আয় বৈষম্য কমানোর ক্ষেত্রে ব্যাংক নিম্নলিখিত অগ্রণী ভূমিকা পালন করছেঃ
→ ব্যাংক প্রান্তিক জন গোষ্ঠীকে স্বল্প সুদে ঋণদানের মাধ্যমে বাংলাদেশের আর্থিকখাতে অন্তর্ভূক্ত করতে পারে। → সিএসআর কার্যক্রমের মাধ্যমে ব্যাংকগুলো উৎপাদনশীল খাতে বিনিয়োগ করে মানুষের কর্মসংস্থানের সৃষ্টি করতে পারে। → ঋণ দানের ক্ষেত্রে গরীবদের বিনা জামানতে ঋণদান করতে হবে এবং ধনীদের উপর (তাদের লাভের উপর) করারোপ করতে পারে।
→ কর্মসংস্থান সৃষ্টির মাধ্যমে আয় বৈষম্য কমাতে পারে।
→ গরীবদের ঋণ দানের ক্ষেত্রে ব্যাংক সহনীয় সুদের হার নির্ধারণ করে তাদের কর্মসংস্থান সৃষ্টিতে সহায়তা করতে পারে। → প্রান্তিক জনগোষ্ঠি যেমনঃ প্রতিবন্ধী, ভিক্ষুক তথাপি সমাজের অবহেলিত জনগোষ্ঠীকে ব্যাংকিং ক্ষেত্রে অন্তর্ভূক্তিকরনের মাধ্যমে তাদের আয় বৃদ্ধিতে সহায়ক হতে পারে।
Question 06.Translation into English:
আপনার বাড়ির পাশেই অযত্নে-অবহেলায় গাছগাছালি মাথা তুলে দাঁড়িয়ে থাকে। অনেক সময় আপনি নিজেই হয়তো শখ করে কিছু গাছ লাগান। আপনি কি জানেন, এ গাছ দেশের অর্থনীতিকে সমৃদ্ধ করছে? চারা গাছ লাগানো থেকে শুরু করে লালন-পালন, পরে কাঠ তৈরি, শেষ পর্যন্ত সেই কাঠ দিয়ে আসবাব তৈরির প্রতিটি পদে অর্থনীতিতে মূল্য সংযোজন হচ্ছে। এ শখের গাছই বছর শেষে মোট দেশজ উৎপাদনের (জিডিপি) সঙ্গে যুক্ত হয়ে অর্থনীতিকে সমৃদ্ধ করছে। জিডিপিতে গাছের অবদান কেমন এ সংক্রান্ত সমীক্ষায় দেখা গেছে, পরিবার পর্যায়ে অর্থাৎ বাড়ির আশেপাশে যে গাছ লাগানো হয়, তা থেকে অর্থনীতিতে বছরে ১২ হাজার ৩৯০ কোটি টাকার মূল্য সংযোজন হয়। বর্তমানে দেশের ২০ লাখ ৫৯ হাজার ৬০৮টি পরিবার এভাবে গাছ লাগিয়ে অর্থনীতিকে সমৃদ্ধ করছে। মূলত গাছ থেকে কাঠ, লাকড়ি ও রাবার হয়, পরে তা বিক্রি করে অর্থ উপার্জন করে এসব পরিবার। আর উৎপাদন থেকে বিক্রি পর্যন্ত যে মূল্য সংযোজন হয়, তাই জিডিপিতে অবদান রাখে। পরিবার পর্যায়ে যত গাছপালা রোপন করা হয়, এর মধ্যে শুধু বাসাবাড়ির আশেপাশেই অর্ধেকের বেশি অর্থাৎ ৫৪ শতাংশ গাছ লাগানো হয়। পরিবার পর্যায়ে বৃক্ষরোপন, পরিচর্যাসহ বিভিন্ন কাজে বিপুলসংখ্যক কর্মসংস্থানও হয়। তাই দেশের অর্থনৈতিক উন্নয়নকে ত্বরান্বিত করার জন্য সামাজিক বনায়ন ও বৃক্ষরোপন আন্দোলনে আমাদের সকলের অংশগ্রহণ একান্ত প্রয়োজন। এ বিষয়ে জনসচেতনতা তৈরীর জন্য গণমাধ্যম তাদের চলমান প্রচেষ্টাকে আরও বেগবান করে অগ্রণী ভূমিকা পালন করতে পারে।
Solution: Trees behind your house stand raising their heads in uncared and neglected. Sometimes you yourself plant some trees as your wish. Do you know, trees are enriching our economy? Every steps starting from nursery of plants, their attendance, making woods and farniture from woods in fine adds value in the economy. In the end of the year, these trees of hobby make our economy prosperous adding with the gross domestic product. It is found in the study of how trees contributes to our economy that in the family level that means trees that are planted behind our house add value to our economy worth 12 thousand and 390 crore taka. At present 20 lac 59 thousand 608 family is flourishing our economy planting trees. Basically, trees produce woods, logs, rubber, afterwards
these families earn money by selling it. And values that are added from production to sale, contribute to economy. More than 50% that means 54% of the trees which are planted in the family level are planted behind the house. Trees plantation, and in different tasks include accelerate our economic development, our participation in the movement of a forestation and tree plantation is extreme desirable. To make mass awareness relating to this, the mass media can play a prominent role by expediting their continuous efforts.
Question 07.Translation into Bengali:
Traffic accidents strike deadly blows to families and they suck billions of taka out of Bangladesh’s economy. More than 4,000 people die on roads every year. Bangladesh has one of the highest traffic accident rates in the world, with more than 85 deaths for every 10,000 registered motor vehicles. This is around 50 times higher than the rate in most western countries. Case studies on traffic accident found that poor families were more likely than those better off to lose their head of household and suffer immediate economic effects because of road traffic injuries. Road accidents kill and injure people who are young and productive, and therefore have a hidden development impact as well. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), road traffic injuries cause a loss of about 2% of GDP in Bangladesh annually. This is almost equal to the total foreign aid received by Bangladesh in a fiscal year. The losses include direct and indirect expenses, such as medical costs, insurance loss, property damage, family income losses and traffic congestion. Traffic accidents also place huge burden on our healthcare system. A survey shows that one-fifth of injury patients in primary and secondary level hospitals across the country had been involved in a traffic accident. It also shows that more than two-thirds of victims were males aged between 18 and 45. Experts say crashes disproportionately affect the poor, making road safety a vital issue for economic development. Bangladesh is trying to modernize its road network, but population and commerce continue to outpace transport infrastructure, turning roads into death traps.
Solution: সড়ক দুর্ঘটনা একটি পরিবারের জন্য মর্মান্তিক আঘাত এবং এই দুর্ঘটনাগুলো বাংলাদেশের অর্থনীতি থেকে শতশত কোটি টাকা শুষে নেয়। প্রতিবছর ৪০ হাজারেরও বেশি লোক সড়ক দুর্ঘটনায় মারা যায়। বিশ্বের সবচেয়ে বেশি সড়ক দুর্ঘটনার হারের দেশগুলোর মধ্যে বাংলাদেশ একটি, যা প্রতি ১০,০০০ হাজার রেজিস্ট্রিকৃত মটর গাড়ির দুর্ঘটনার ৮৫টিরও বেশি। এই হার অধিকাংশ পশ্চিমা বিশ্বের দেশগুলোর হারের চাইতে প্রায় ৫০গুণ বেশি। সড়ক দুর্ঘটনার উপর কৃত একটি সমীক্ষায় পাওয়া গেছে, অপেক্ষাকৃত দরিদ্র পরিবারগুলো সড়ক দুর্ঘটনায় তাদের পরিবারের উপার্জনকারীকে হারানোর ক্ষেত্রে এগিয়ে এবং এর ফলে তারা আর্থিক সমস্যার সম্মুখীন হয়। সড়ক দুর্ঘটনা যুবক ও উৎপাদনশীল লোকগুলোকে হত্যা করে এবং এই কারণে এটি উন্নয়নের জন্য একটি লুকায়িত বাধাও বটে।
বিশ্ব স্বাস্থ্য সংস্থা অনুযায়ী, সড়ক দুর্ঘটনা বাংলাদেশের বাৎসরিক জিডিপির ২% ক্ষতির কারণ যা কিনা বাংলাদেশ প্রতি বছর আর্থিক যে বৈদেশিক সাহায্য পায় তার সমান। এই সকল ক্ষতির মধ্যে রয়েছে প্রত্যক্ষ ও পরোক্ষ ব্যয় যেমন চিকিৎসা ব্যয়,
ইন্স্যুরেন্স ব্যয়, সম্পদের ক্ষতি, পরিবারের আর্থিক ক্ষতি এবং যানজট। সড়ক দুর্ঘটনা আমাদের স্বাস্থ্য খাতে একটি বিরাট বোঝা। একটি সমীক্ষায় দেখা গিয়েছে যে, প্রাথমিক ও মাধ্যমিক পর্যায়ে আহত রোগীগুলোর মধ্যে হলো সড়ক দুর্ঘটনায়
আহত। এটি আরো দেখিয়েছে যে, – অংশই হলো পুরুষ যাদের বয়স ১৮ থেকে ৪৫ এর মধ্যে। বিশেষজ্ঞদের মতে, এই সকল দুর্ঘটনা অসমভাবে দরিদ্রদের উপর প্রভাব ফেলে, ফলে এটি অর্থনৈতিক উন্নয়নের জন্য একটি বড় বাধা হিসেবে ধরা হয়। বাংলাদেশে তার সড়ক ব্যবস্থাপনা আধুনিকায়নের চেষ্টা করছে। কিন্তু জনসংখ্যা ও ব্যবসায় অবকাঠামোকে ক্ষতি করছে যা একটি মৃত্যুফাঁদে পরিণত হচ্ছে ,


